
Also look up the Pitzer acentric factor, selected compounds, and a more complete list can be found in Reid et al.

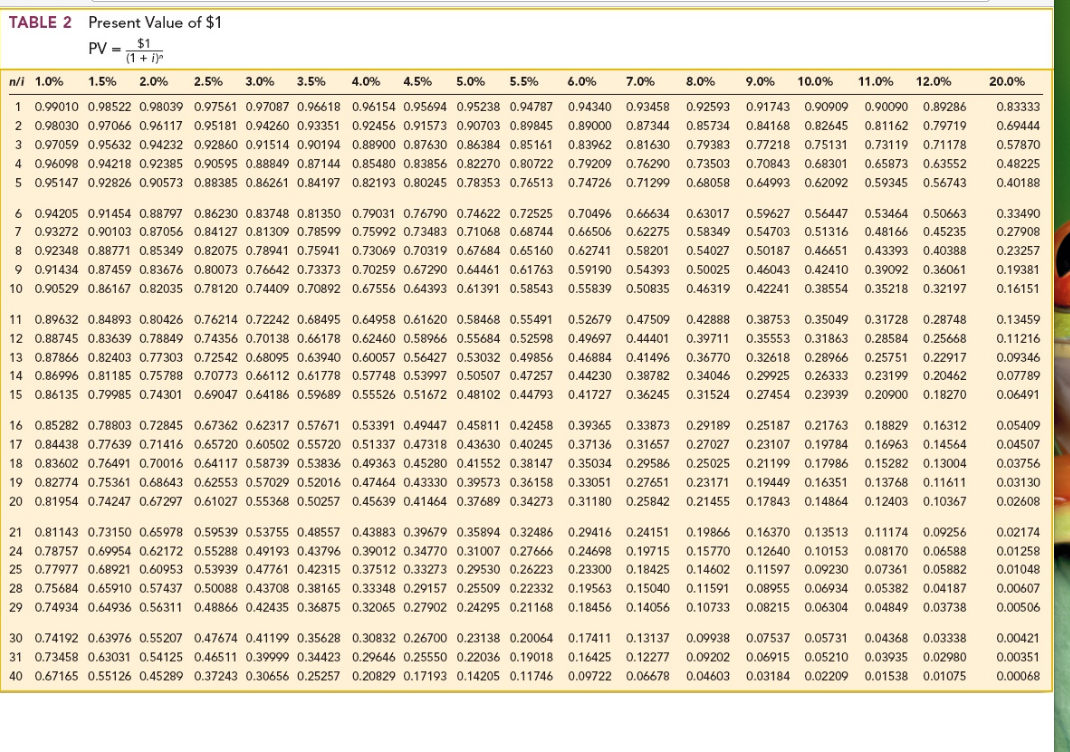
Look up the critical temperature and pressure (Tc and Pc) for the species of interest in Table B.l or elsewhere. Values for this factor at various interest rates and numbers of interest periods are given in Table 1. The term (1 + i)" is commonly referred to as the discrete single-payment compound-amount factor. Table 9-21 contains 5 and 6 percent discrete interest factors. Interest calculated for a given time period is known as discrete compound interest, with discrete referring to a discrete time period. Thus with quinoline it can be easily foreseen from the partial rate factors (Table IX) that not only all the possible 21 diphenylquinoline isomers, but also. If the conversions are high, the mixture of the reaction products becomes much more complex. The other aspect concerns the conversions of the heterocyclic compounds, which are always very low, usually lower than 1%. Thus, for example, quinoline gives all the seven possible isomers in appreciable amounts.This is in contrast to all the homolytic substitutions described in the previous sections, which lead to exclusive attack at the 2- and 4-positions. The first concerns the position of substitution generally all the free positions are substituted, giving very complex mixtures of isomers. The low selectivity affects the synthetic interest of homolytic arylation from two points of view. TABLE 3 Compound Interest Factors Continuous, Uniform Cash Fiow, Continuous Compounding. īy the use of this relationship, the compound interest factors for discrete cash flows compound continuously shown in Table 1 can be derived from the discrete compounding factors in Table 2. Complete tables can be found in the Additional Reading at the end of the chapter.

The numerical values for each factor for selected interest rates can be found in the tables at the end of this chapter. AH of these factors can be found in Table 1, including algebraic and functional formats and the Excel functions. The compound interest factors described in this section are used for discrete cash flows compounded discretely at the end of each interest period. TABLE 1 Compound Interest Factors Discrete Cash Flow, Discrete Compounding. Following is a summary showing the significance and meaning of the compounding factors presented in Table 3, Derivations of the factors are presented in the text. (12), the common interest expressions can be written in simplified form by using discount-factor and compound-interest-factor notation. Table 9-3 gives examples of compound-interest factors and example compound-interest calculations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
